Cyber security refers to every aspect of protecting an organization and its employees and assets against cyber threats. As cyberattacks become more common and sophisticated and corporate networks grow more complex, a variety of cyber security solutions are required to mitigate corporate cyber risk.
The Different Types of Cybersecurity
Cyber security is a wide field covering several disciplines. It can be divided into seven main pillars:
1. Network Security
Most attacks occur over the network, and network security solutions are designed to identify and block these attacks. These solutions include data and access controls such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP), IAM (Identity Access Management), NAC (Network Access Control), and NGFW (Next-Generation Firewall) application controls to enforce safe web use policies.
Advanced and multi-layered network threat prevention technologies include IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), NGAV (Next-Gen Antivirus), Sandboxing, and CDR (Content Disarm and Reconstruction). Also important are network analytics, threat hunting, and automated SOAR (Security Orchestration and Response) technologies.

2. Cloud Security
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, securing the cloud becomes a major priority. A cloud security strategy includes cyber security solutions, controls, policies, and services that help to protect an organization’s entire cloud deployment (applications, data, infrastructure, etc.) against attack.
While many cloud providers offer security solutions, these are often inadequate to the task of achieving enterprise-grade security in the cloud. Supplementary third-party solutions are necessary to protect against data breaches and targeted attacks in cloud environments.

3. Endpoint Security
The zero-trust security model prescribes creating micro-segments around data wherever it may be. One way to do that with a mobile workforce is using endpoint security. With endpoint security, companies can secure end-user devices such as desktops and laptops with data and network security controls, advanced threat prevention such as anti-phishing and anti-ransomware, and technologies that provide forensics such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.

4. Mobile Security
Often overlooked, mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones have access to corporate data, exposing businesses to threats from malicious apps, zero-day, phishing, and IM (Instant Messaging) attacks. Mobile security prevents these attacks and secures the operating systems and devices from rooting and jailbreaking. When included with an MDM (Mobile Device Management) solution, this enables enterprises to ensure only compliant mobile devices have access to corporate assets.

5. IoT Security
While using Internet of Things (IoT) devices certainly delivers productivity benefits, it also exposes organizations to new cyber threats. Threat actors seek out vulnerable devices inadvertently connected to the Internet for nefarious uses such as a pathway into a corporate network or for another bot in a global bot network.
IoT security protects these devices with discovery and classification of the connected devices, auto-segmentation to control network activities, and using IPS as a virtual patch to prevent exploits against vulnerable IoT devices. In some cases, the firmware of the device can also be augmented with small agents to prevent exploits and runtime attacks.
6. Application Security
Web applications, like anything else directly connected to the Internet, are targets for threat actors. Since 2007, OWASP has tracked the top 10 threats to critical web application security flaws such as injection, broken authentication, misconfiguration, and cross-site scripting to name a few.

With application security, the OWASP Top 10 attacks can be stopped. Application security also prevents bot attacks and stops any malicious interaction with applications and APIs. With continuous learning, apps will remain protected even as DevOps releases new content.
7. Zero Trust
The traditional security model is perimeter-focused, building walls around an organization’s valuable assets like a castle. However, this approach has several issues, such as the potential for insider threats and the rapid dissolution of the network perimeter.
As corporate assets move off-premises as part of cloud adoption and remote work, a new approach to security is needed. Zero trust takes a more granular approach to security, protecting individual resources through a combination of micro-segmentation, monitoring, and enforcement of role-based access controls.

The Evolution of the Cyber Security Threat Landscape
The cyber threats of today are not the same as even a few years ago. As the cyber threat landscape changes, organizations need protection against cybercriminals’ current and future tools and techniques.
Gen V Attacks
The cyber security threat landscape is continually evolving, and, occasionally, these advancements represent a new generation of cyber threats. To date, we have experienced five generations of cyber threats and solutions designed to mitigate them, including:
- Gen I (Virus): In the late 1980s, virus attacks against standalone computers inspired the creation of the first antivirus solutions.
- Gen II (Network): As cyberattacks began to come over the Internet, the firewall was developed to identify and block them.
- Gen III (Applications): Exploitation of vulnerabilities within applications caused the mass adoption of intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
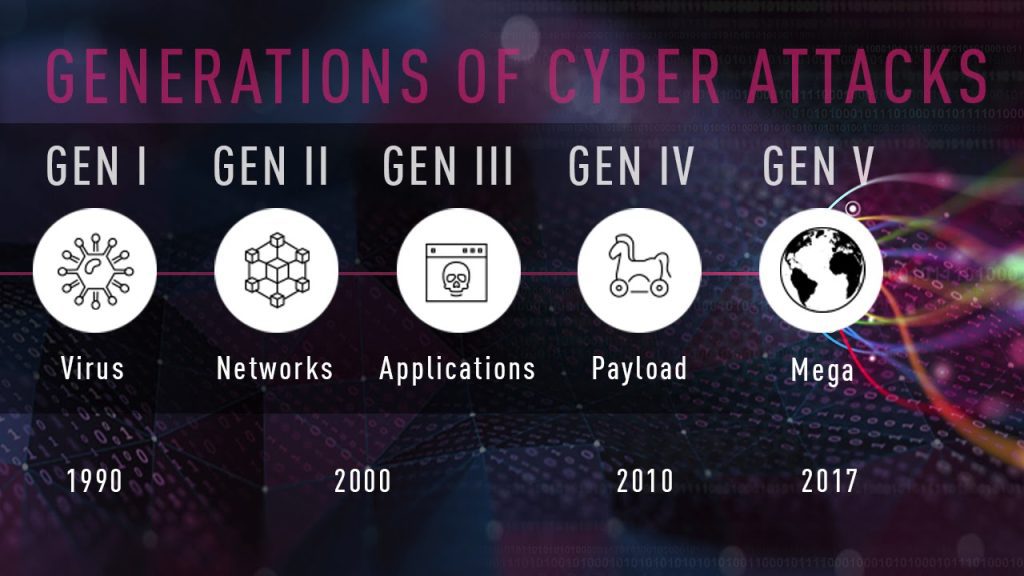
Gen IV (Payload): As malware became more targeted and able to evade signature-based defenses, anti-bot and sandboxing solutions were necessary to detect novel threats.
Gen V (Mega): The latest generation of cyber threats uses large-scale, multi-vectors attacks, making advanced threat prevention solutions a priority.
Each generation of cyber threats made previous cyber security solutions less effective or essentially obsolete. Protecting against the modern cyber threat landscape requires Gen V cyber security solutions.
Supply Chain Attacks
Historically, many organizations’ security efforts have been focused on their own applications and systems. By hardening the perimeter and only permitting access to authorized users and applications, they try to prevent cyber threat actors from breaching their networks.
Recently, a surge in supply chain attacks has demonstrated the limitations of this approach and cybercriminals’ willingness and ability to exploit them. Incidents like the SolarWinds, Microsoft Exchange Server, and Kaseya hacks demonstrated that trust relationships with other organizations can be a weakness in a corporate cyber security strategy.
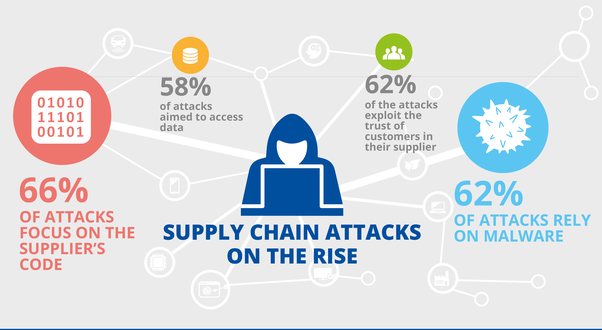
By exploiting one organization and leveraging these trust relationships, a cyber threat actor can gain access to the networks of all of their customers.
Protecting against supply chain attacks requires a zero trust approach to security. While partnerships and vendor relationships are good for business, third-party users and software should have access limited to the minimum necessary to do their jobs and should be continually monitored.
Types of Cyber Threats
The threats countered by cyber-security are three-fold:
- Cyber crime includes single actors or groups targeting systems for financial gain or to cause disruption.
- Cyber-attack often involves politically motivated information gathering.
- Cyber-terrorism is intended to undermine electronic systems to cause panic or fear.
Common cyber threats include:
- Malware, such as ransomware, botnet software, RATs (remote access Trojans), rootkits and bootkits, spyware, Trojans, viruses, and worms.
- Backdoors, which allow remote access.
- Form jacking, which inserts malicious code into online forms.
- Crypto jacking, which installs illicit cryptocurrency mining software.
- SQL injection, An SQL (structured language query) injection is a type of cyber-attack used to take control of and steal data from a database.
- DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) attacks, which flood servers, systems, and networks with traffic to knock them offline.
- DNS (domain name system) poisoning attacks, which compromise the DNS to redirect traffic to malicious sites.
The Need for a Consolidated Cyber Security Architecture
In the past, organizations could get by with an array of standalone security solutions designed to address specific threats and use cases. Malware attacks were less common and less sophisticated, and corporate infrastructures were less complex.
Today, cyber security teams are often overwhelmed while trying to manage these complex cyber security architectures.

This is caused by a number of factors, including:
- Sophisticated Attacks: Modern cyberattacks can no longer be detected with legacy approaches to cyber security. More in-depth visibility and investigation is necessary to identify campaigns by advanced persistent threats (APTs) and other sophisticated cyber threat actors.
- Complex Environments: The modern corporate network sprawls over on-prem infrastructure and multiple cloud environments. This makes consistent security monitoring and policy enforcement across an organization’s entire IT infrastructure much more difficult.
- Heterogeneous Endpoints: IT is no longer limited to traditional desktop and laptop computers. Technological evolution and bring your own device (BYOD) policies make it necessary to secure a range of devices, some of which the company does not even own.
- Rise of Remote Work: The response to the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated that remote and hybrid work models were viable for many companies. Now, organizations need solutions that allow them to effectively protect the remote workforce as well as on-site employees.
Trying to solve all of these challenges with an array of disconnected solutions is unscalable and unsustainable. Only by consolidating and streamlining their security architectures can companies effectively manage their cyber security risk.
Achieving Comprehensive Cybersecurity with Check Point
A modern cybersecurity infrastructure is one that is consolidated and built from solutions that are designed to work together. This requires partnering with a security provider with experience in protecting all of an organization’s assets against a range of cyber threats.
Check Point offers solutions for all of an organization’s security needs, including:
- Network Security: Check Point Quantum
- IoT Security: Check Point Quantum IoT Protect
- Cloud Security: Check Point Cloud Guard
- Application Security: Check Point Cloud Guard App Sec
- Endpoint Security: Check Point Harmony Endpoint
- Mobile Security: Check Point Harmony Mobile

Latest Cyber Threats
What are the latest cyber threats that individuals and organizations need to guard against? Here are some of the most recent cyber threats that the U.K., U.S., and Australian governments have reported on.
Dridex Malware
In December 2019, the U.S. Department of Justice charged the leader of an organized cyber-criminal group for their part in a global Dridex malware attack. This malicious campaign affected the public, government, infrastructure and business worldwide.
Dridex is a financial trojan with a range of capabilities. Affecting victims since 2014, it infects computers though phishing emails or existing malware. Capable of stealing passwords, banking details and personal data which can be used in fraudulent transactions, it has caused massive financial losses amounting to hundreds of millions.

In response to the Dridex attacks, the U.K.’s National Cyber Security Centre advises the public to “ensure devices are patched, anti-virus is turned on and up to date and files are backed up”.
Romance scams
In February 2020, the FBI warned U.S. citizens to be aware of confidence fraud that cybercriminals commit using dating sites, chat rooms and apps. Perpetrators take advantage of people seeking new partners, duping victims into giving away personal data.
The FBI reports that romance cyber threats affected 114 victims in New Mexico in 2019, with financial losses amounting to $1.6 million.

Emotet Malware
In late 2019, The Australian Cyber Security Centre warned national organizations about a widespread global cyber threat from Emotet malware.
Emotet is a sophisticated trojan that can steal data and also load other malware. Emotet thrives on unsophisticated password: a reminder of the importance of creating a secure password to guard against cyber threats.

End-User Protection
End-user protection or endpoint security is a crucial aspect of cyber security. After all, it is often an individual (the end-user) who accidentally uploads malware or another form of cyber threat to their desktop, laptop or mobile device.
So, how do cyber-security measures protect end users and systems? First, cyber-security relies on cryptographic protocols to encrypt emails, files, and other critical data. This not only protects information in transit, but also guards against loss or theft.
In addition, end-user security software scans computers for pieces of malicious code, quarantines this code, and then removes it from the machine. Security programs can even detect and remove malicious code hidden in Master Boot Record (MBR) and are designed to encrypt or wipe data from computer’s hard drive.

Electronic security protocols also focus on real-time malware detection. Many use heuristic and behavioral analysis to monitor the behavior of a program and its code to defend against viruses or Trojans that change their shape with each execution (polymorphic and metamorphic malware). Security programs can confine potentially malicious programs to a virtual bubble separate from a user’s network to analyze their behavior and learn how to better detect new infections.
Security programs continue to evolve new defenses as cyber-security professionals identify new threats and new ways to combat them. To make the most of end-user security software, employees need to be educated about how to use it. Crucially, keeping it running and updating it frequently ensures that it can protect users against the latest cyber threats.
Cyber Safety Tips – Protect Yourself Against Cyber Attacks
How can businesses and individuals guard against cyber threats? Here are our top cyber safety tips:
- Update your software and operating system: This means you benefit from the latest security patches.
- Use anti-virus software: Security solutions like Kaspersky Total Security will detect and removes threats. Keep your software updated for the best level of protection.
- Use strong passwords: Ensure your passwords are not easily guessable.
- Do not open email attachments from unknown senders: These could be infected with malware.
- Do not click on links in emails from unknown senders or unfamiliar websites: This is a common way that malware is spread.

- Avoid using unsecure Wi Fi networks in public places: Unsecure networks leave you vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks.
Kaspersky Endpoint Security received three AV-TEST awards for the best performance, protection, and usability for a corporate endpoint security product in 2021. In all tests Kaspersky Endpoint Security showed outstanding performance, protection, and usability for businesses.
The Advantages of Cyber Security
Today’s cyber security industry is primarily focused on protecting devices and systems from attackers. While the bits and bytes behind these efforts can be hard to visualize, it’s much easier to consider the effects. Without cyber security professionals working tirelessly, many websites would be nearly impossible to enjoy due to ever-present denial-of-service attack attempts. Imagine not having access to Simplilearn’s community of experts and certified professionals — no more tips, tricks, and advice to help you achieve your professional goals!
Without solid cyber security defenses, it would be easy to destroy modern-day essentials like the power grids and water treatment facilities that keep the world running smoothly.
Simply put, cyber security is critically important because it helps to preserve the lifestyles we have come to know and enjoy.
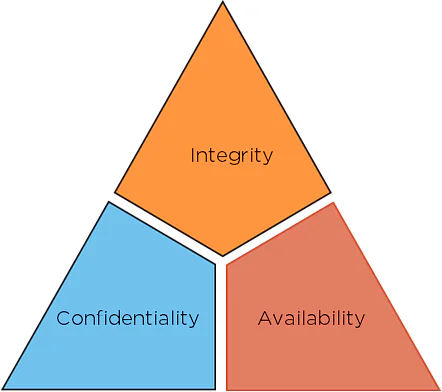
CIA Triad
The security of any organization starts with three principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability. This is called as CIA, which has served as the industry standard for computer security since the time of first mainframes.
Cyber Security Expert?
As data breaches, hacking, and cybercrime reach new heights, companies are increasingly relying on Cyber Security experts to identify potential threats and protect valuable data. It makes sense that the Cyber Security market is expected to grow from $152 billion in 2018 to $248 billion by 2023.
So what do Cyber Security experts do? On any given day, they:
- Find, test, and repair weaknesses within a company’s infrastructure.
- Monitor systems for malicious content
- Identify network breaches
- Install regular software updates, firewalls, and antivirus protection
- Strengthen areas where attacks may have occurred
They work in one or more of these common Cyber Security domains to keep data safe:
- Asset security: Analyze networks, computers, routers, and wireless access points
- Security architecture and engineering: Standardize security policies and procedures
- Communication and network security: Regulate cloud storage and data transfer
- Identity and access management: Track user authentication and accountability
- Security operations: Monitor security to identify attacks
- Security assessment and testing: Test security policies to ensure compliance with industry standards
- Software development security: Create and repeatedly test code
- Security and risk management: Identify potential risks and implement appropriate security controls
Cyber Security experts employ different tactics to secure computer systems and networks. Some of the best practices include:
- Using two-way authentication
- Securing passwords
- Installing regular updates
- Running antivirus software
- Using firewalls to disable unwanted services
- Avoiding phishing scams
- Employing cryptography, or encryption
- Securing domain name servers, or DNS
Cyber Security Professionals?
A leading cyber security professional doesn’t necessarily need to boast a traditional academic background. Due to this fact, certifications have become an industry-standard marker of knowledge and proficiency, and this has led to the development of many options for those who want to upskill for a promising career in cyber security.
Are you looking for expert instruction at an affordable price? Simplilearn offers several certification-focused courses that are accessible to everyone, regardless of their background. Some of our most popular courses include:
Certified Ethical Hacking (CEH) Certification
Have you ever wanted to learn how to hack into networks but are wary of the prospect of getting into trouble? Our CEH Certification will show you that ethical hacking skills can be an entry point into a meaningful and exciting career path.
CISSP Certification
This course will show you everything you need to know to become a Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP). CISSP Certification is one of the most sought-after credentials in today’s cyber security job market. A small investment in this training can have an impact on the trajectory of your career.
Cyber Security Expert
Once you’ve mastered the fundamentals of information technology and networking, you’ll be ready to become a Cyber Security Expert. As an advanced course, it offers experienced professionals an excellent opportunity to expand their cyber toolset, laying out a program for those who are motivated to reach lofty career goals in the cyber security industry.
Why Not Become a Cyber Security Expert?
There is a critical and growing need for qualified cybersecurity professionals today. There is also a shortage of those, which means that there is a giant opportunity to get in on this field. Whether you are just starting out, looking to boost your existing skills and credentials, or changing your career because you are looking for a new challenge, check out Simplilearn’s Post Graduate Program in Cyber Security, which can help attain your goals.
With top-class industry partnerships, university alliances, and accreditation by globally recognized industry accreditation bodies, you can find what you need with Simplilearn.
Computer – KnowledgeSthali


Good post and right to the point. I am not sure if this is actually the best place to ask but do you people have any ideea where to get some professional writers? Thanks 🙂