A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought, idea, or statement. It typically consists of a subject and a predicate, where the subject is the doer of the action, and the predicate is the action or state of being. Sentences serve as a fundamental unit of communication and can convey information, ask questions, make statements, or express emotions. Here are examples of different types of sentences:
- Declarative Sentence (Statement):
- The sun sets in the west.
- Interrogative Sentence (Question):
- Did you finish your homework?
- Imperative Sentence (Command):
- Please close the door.
- Exclamatory Sentence (Expressing Strong Emotion):
- What a beautiful sunset!
A complete sentence must have a subject and a verb, and it should convey a clear and complete idea. Sentences come in various forms and lengths, contributing to the richness and diversity of written and spoken language.
Formation of Sentences
The formation of sentences involves constructing grammatically correct and meaningful sequences of words to convey ideas or communicate information. Here are key elements and guidelines for forming sentences:
- Subject and Predicate:
- Every sentence should have a subject (the doer of the action) and a predicate (the action or state of being). This is the basic structure of a sentence.
- Example: She (subject) reads books every day (predicate).
- Every sentence should have a subject (the doer of the action) and a predicate (the action or state of being). This is the basic structure of a sentence.
- Word Order:
- In English, the typical word order is Subject-Verb-Object (SVO), but this can vary based on sentence structure and emphasis.
- Example: The cat (subject) chased (verb) the mouse (object).
- In English, the typical word order is Subject-Verb-Object (SVO), but this can vary based on sentence structure and emphasis.
- Complete Thoughts:
- A sentence should express a complete thought, idea, or statement. It should make sense on its own.
- Example: The sun sets in the west.
- A sentence should express a complete thought, idea, or statement. It should make sense on its own.
- Punctuation:
- Proper use of punctuation marks, such as periods, commas, question marks, and exclamation points, is essential for clarity and to indicate the structure of a sentence.
- Example: Have you finished your homework?
- Proper use of punctuation marks, such as periods, commas, question marks, and exclamation points, is essential for clarity and to indicate the structure of a sentence.
- Varied Sentence Structure:
- Using a variety of sentence structures (simple, compound, complex) adds richness and complexity to writing.
- Example:
- She likes reading books.
- Although she prefers fiction, she occasionally reads non-fiction.
- Example:
- Using a variety of sentence structures (simple, compound, complex) adds richness and complexity to writing.
- Conjunctions:
- Conjunctions like and, but, or, so, yet can be used to connect ideas and create compound or complex sentences.
- Example: He wanted to go to the party, but he had to finish his work.
- Conjunctions like and, but, or, so, yet can be used to connect ideas and create compound or complex sentences.
- Consistency and Clarity:
- Sentences should be clear, concise, and maintain a consistent tone and style.
- Vocabulary and Diction:
- Choose appropriate words and use varied vocabulary to convey meaning effectively.
By combining these elements, writers can create sentences that effectively communicate their intended message in a coherent and grammatically correct manner.
Parts of a Sentence
The basic division of sentences is in terms of,
- Subjects – A noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that does the action mentioned in the sentence. It mostly occurs at the beginning of the sentence.
- Predicates – The remaining part of the sentence. It begins with the verb.
Here are a few examples.
Example 1: Daisy teaches English.
- Daisy (Subject)
- Teaches English (Predicate)
Example 2:
Anitha called me yesterday.
- Anitha (Subject)
- Called me yesterday (Predicate)
Example 3: The girl wearing the yellow dress is my new neighbour.
- The girl wearing the yellow dress (Subject)
- Is my new neighbour (Predicate)
Understanding the division of sentences into subjects and predicates is fundamental to analyzing sentence structure and constructing well-formed sentences. Great examples!
Structure of a sentence
A sentence consists of various components that work together to convey meaning. Here are the key components of a sentence:
- Subject:
- The subject is the main noun or pronoun that performs the action or is the focus of the sentence.
- Example: The cat sat on the windowsill.
- Predicate:
- The predicate contains the verb and provides information about the subject, expressing what the subject is doing or the state of being.
- Example: The cat sat on the windowsill.
- Verb:
- The verb is a word that expresses action or a state of being. It is a crucial part of the predicate.
- Example: The cat sat on the windowsill.
- Object:
- An object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb. There are direct objects, indirect objects, and objects of prepositions.
- Example: She gave him a gift. (him is the indirect object)
- Complement:
- A complement is a word or group of words that completes the meaning of the predicate. It includes predicate nominatives and predicate adjectives.
- Example: She is a doctor. (a doctor is a predicate nominative)
- Modifiers:
- Modifiers are words or phrases that provide additional information about other elements in the sentence, such as adjectives and adverbs.
- Example: The tall man walked quickly to the store.
- Conjunctions:
- Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence.
- Example: I like both tea and coffee.
- Prepositions:
- Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other elements in a sentence.
- Example: The book is on the shelf.
- Interjections:
- Interjections are words used to express strong emotions or reactions.
- Example: Wow, that’s amazing!
Understanding how these components work together helps in constructing clear and effective sentences. Each element plays a specific role in conveying meaning and ensuring grammatical correctness.
The Different Types of Sentences
There are four main types of sentences based on their functions: declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory. Additionally, each of these types can be further classified into different forms. Based on Structure: Simple Sentences, Compound Sentences, Complex Sentences, Compound-Complex Sentences.
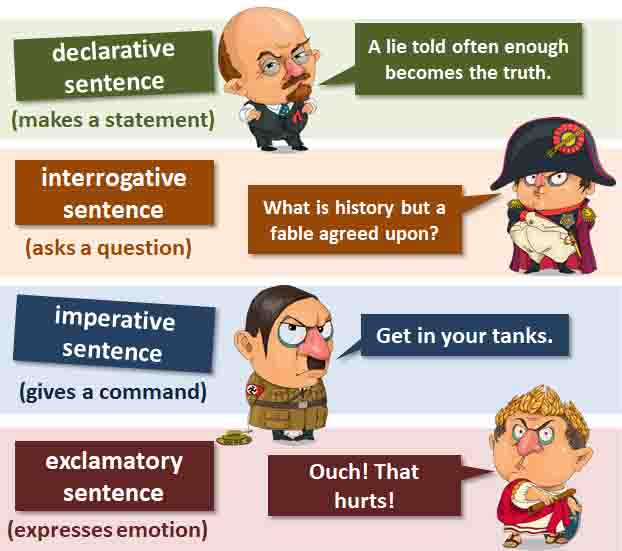
1. Declarative Sentences:
- Makes a statement or expresses an opinion.
- Example: The sun sets in the west.
2. Interrogative Sentences:
- Asks a question.
- Example: Did you finish your homework?
3. Imperative Sentences:
- Gives a command or makes a request.
- Example: Please close the door.
4. Exclamatory Sentences:
- Expresses strong emotion or excitement.
- Example: What a beautiful sunset!
5. Simple Sentences:
- Contains one independent clause.
- Example: She reads books.
6. Compound Sentences:
- Contains two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction or a semicolon.
- Example: She reads books, and he writes poems.
7. Complex Sentences:
- Contains one independent clause and at least one dependent clause.
- Example: Although she prefers fiction, she occasionally reads non-fiction.
8. Compound-Complex Sentences:
- Contains two or more independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
- Example: She reads books, and he writes poems when they have free time.
Why Understanding Sentences Is Important?
Understanding sentences is crucial for effective communication and language comprehension. Here are several reasons why understanding sentences is important:
- Communication:
- Sentences are the building blocks of communication. Understanding sentences allows individuals to convey thoughts, ideas, and information to others in a clear and coherent manner.
- Expressing Ideas:
- Sentences enable individuals to express complex thoughts and ideas. Proper sentence construction ensures that the intended message is accurately conveyed.
- Reading Comprehension:
- Reading involves understanding sentences and their structures. Proficient sentence comprehension is essential for grasping the meaning of written texts, whether they are books, articles, or any other form of written communication.
- Writing Skills:
- Effective writing requires a strong understanding of sentence structure. This includes knowing how to create grammatically correct sentences, use punctuation appropriately, and organize ideas coherently.
- Academic Success:
- In educational settings, understanding sentences is crucial for success in various subjects. It is fundamental to tasks such as reading comprehension, essay writing, and critical analysis.
- Professional Communication:
- In professional settings, clear and concise sentence construction is vital for effective communication. Well-structured sentences contribute to professional emails, reports, presentations, and other forms of business communication.
- Grammar and Language Proficiency:
- A solid understanding of sentences is foundational to mastering grammar and language proficiency. It helps individuals use words, phrases, and clauses appropriately, enhancing overall language skills.
- Logical Reasoning:
- Sentences convey logical relationships and connections between ideas. Understanding sentence structure aids in logical reasoning and the ability to follow or construct logical arguments.
- Critical Thinking:
- Analyzing sentences promotes critical thinking skills. It involves evaluating the meaning, intent, and implications of statements, fostering a deeper understanding of information.
- Effective Communication Skills:
- Understanding sentences contributes to the development of effective communication skills, including active listening, responding appropriately, and engaging in meaningful conversations.
In summary, understanding sentences is foundational to effective communication, literacy, academic success, and professional development. It plays a central role in various aspects of language use and contributes to overall language proficiency.
See this also –
- Interjection: Definition, Types, and 100+ Examples
- Alphabet: Definition, Vowels, and Consonants
- Clause: Definition, Types and 50+ Examples
- Past Tense: Definition, Types, and 100+ Examples
- भारतीय संविधान के 22 भाग और 395 अनुच्छेदों की जानकारी
- पृथ्वी के प्रमुख क्षेत्र | परिमंडल | Earth’s Domain | Circle
- कोरियाई युद्ध |1950-1953

